Introduction
Check out these 2 short videos to learn about the existing data problems that Alluxio is designed to solve and where Alluxio sits in the big data ecosystem:
- ▶️ The Problem To Be Solved (3:06)
- ▶️ What Is Alluxio? (2:50)
About Alluxio
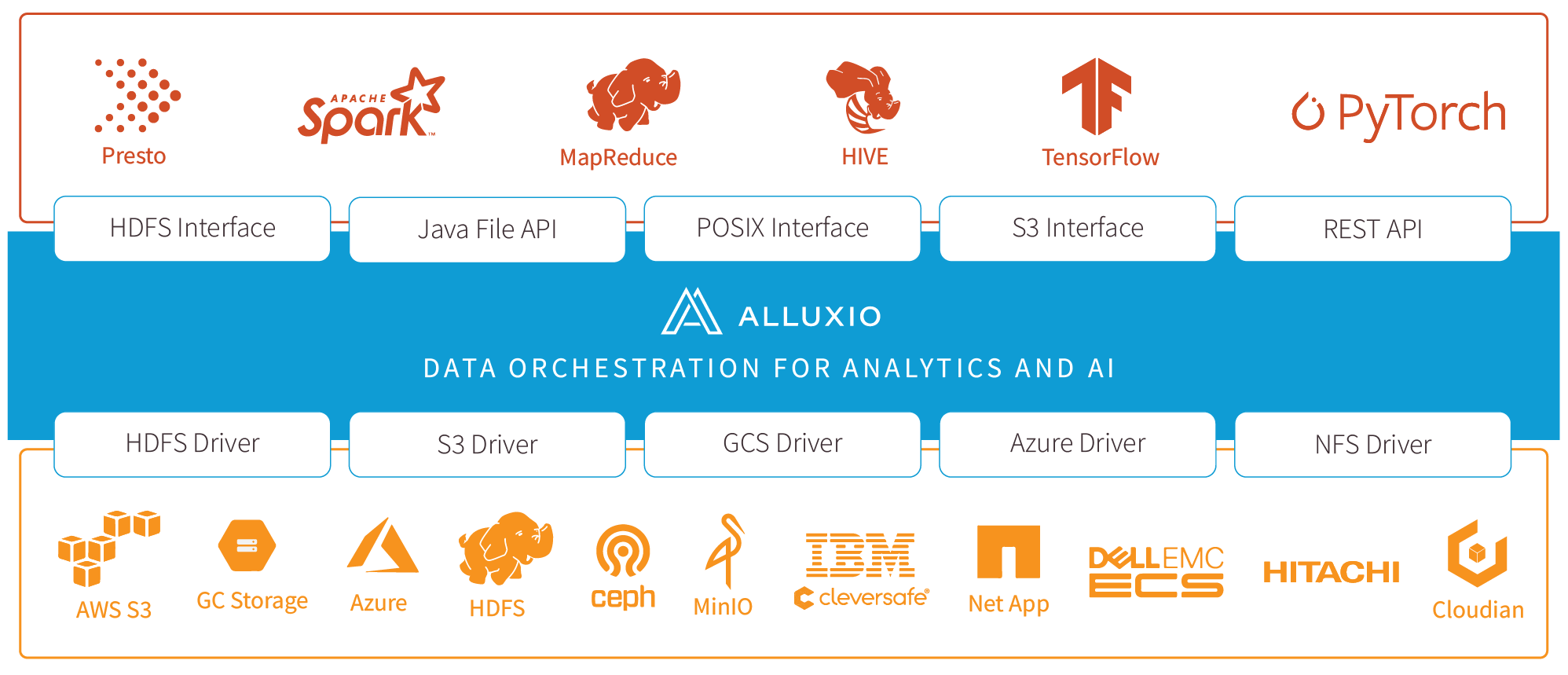
Alluxio is world’s first open source data orchestration technology for analytics and AI for the cloud. It bridges the gap between data driven applications and storage systems, bringing data from the storage tier closer to the data driven applications and makes it easily accessible enabling applications to connect to numerous storage systems through a common interface. Alluxio’s memory-first tiered architecture enables data access at speeds orders of magnitude faster than existing solutions.
In the data ecosystem, Alluxio lies between data driven applications, such as Apache Spark, Presto, Tensorflow, Apache HBase, Apache Hive, or Apache Flink, and various persistent storage systems, such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, HDFS, IBM Cleversafe, EMC ECS, Ceph, NFS, Minio, and Alibaba OSS. Alluxio unifies the data stored in these different storage systems, presenting unified client APIs and a global namespace to its upper layer data driven applications.
The Alluxio project originated from the UC Berkeley AMPLab (see papers) as the data access layer of the Berkeley Data Analytics Stack (BDAS). It is open source under Apache License 2.0. Alluxio is one of the fastest growing open source projects that has attracted more than 1000 contributors from over 300 institutions including Alibaba, Alluxio, Baidu, CMU, Google, IBM, Intel, NJU, Red Hat, Tencent, UC Berkeley, and Yahoo.
Today, Alluxio is deployed in production by hundreds of organizations with the largest deployment exceeding 1,500 nodes.
Dora Architecture
Dora, short for Decentralized Object Repository Architecture, is the foundation of the Alluxio system.
As an open-source distributed caching storage system, Dora offers low latency, high throughput, and cost savings, while aiming to provide a unified data layer that can support various data workloads, including AI and data analytics.
Dora leverages decentralized storage and metadata management to provide higher performance and availability, as well as pluggable data security and governance, enabling better scalability and more efficient management of large-scale data access.
Dora’s architecture goal:
- Scalability: Scalability is a top priority for Dora, which needs to support billions of files to meet the demands of data-intensive applications, such as AI training.
- High Availability: Dora’s architecture is designed with high availability in mind, with 99.99% uptime and protection against single points of failure.
- Performance: Performance is a key goal for Dora, which prioritizes Presto/Trino powered SQL analytics workloads and GPU utilization for AI workloads.
The diagram below shows the architecture design of Dora, which consists of four major components: the service registry, scheduler, client, and worker.
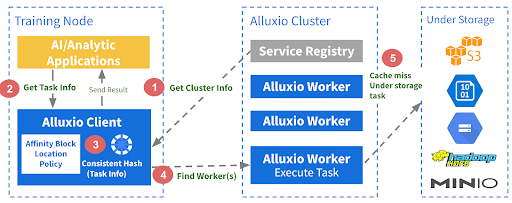
- The worker is the most important component, as it stores both metadata and data that are sharded by key, usually the path of the file.
- The client runs inside the applications and utilizes the same consistent hash algorithm to determine the appropriate worker for the corresponding file.
- The service registry is responsible for service discovery and maintains a list of workers.
- The scheduler handles all asynchronous jobs, such as preloading data to workers.
Alluxio Community Slack
Join our vibrant and fast-growing Alluxio Community Slack Channel to connect with users & developers of Alluxio. If you need help running Alluxio or encounter any blockers, send your technical questions to our #troubleshooting channel. If you are a developer looking to contribute to Alluxio, check out the #dev channel.



